Into Data Science
🎯 Module Overview
This module enabled me to:
- Critically evaluate key Business Intelligence (BI) concepts and tools.
- Understand the application of dashboards and reporting systems in enterprise contexts.
- Engage in continuous professional development in the domain of data science.
- Explore stakeholder perspectives in aligning data strategies with business objectives.
- Assess data policies and regulatory frameworks for enterprise data compliance.
📚 Table of Contents
- Unit 1: Introduction to Data Science
- Unit 2: Enterprise Data Architecture
- Unit 3: Data Pipeline
- Unit 4: Big Data Architecture
- Unit 5: Analytics Tools
- Unit 6: Value of Data
- Unit 7: IP Strategy
- Unit 8: Digital Transformation
- Unit 9: Compliance & Ethics
- Unit 10: ITIL Framework
- Unit 11: Business Intelligence
- Unit 12: ERP Systems
Unit 1: Introduction to Data Science
💬 “Data science is the engine of digital transformation.”
Key Concepts:
- Foundations of data architecture and data pipelines
- Business Intelligence as a strategic tool
- Role of AI, IoT, Cloud, and Blockchain in data ecosystems
Reflections: This unit introduced the foundational role of data science in modern enterprises. I examined how structured data systems underpin decision-making, and reflected on the convergence of cybersecurity, AI, and machine learning, particularly through the lens of machine learning and anomaly detection combatting modern digital threats.
Related Work:
Unit 2: Enterprise Data Architecture
Key Concepts:
- Conceptual vs Logical vs Physical architecture
- Business, Application, Information, and Technology layers
- Data governance and secure flows
Reflections: I gained clarity on how Enterprise Data Architecture (EDA) is used to structure and manage enterprise data assets, differentiating between its conceptual, logical, and physical components. It helped me see how architecture supports strategic alignment and how crucial understanding data flows, processes, storage, and security is for effective data management.
Related Work:
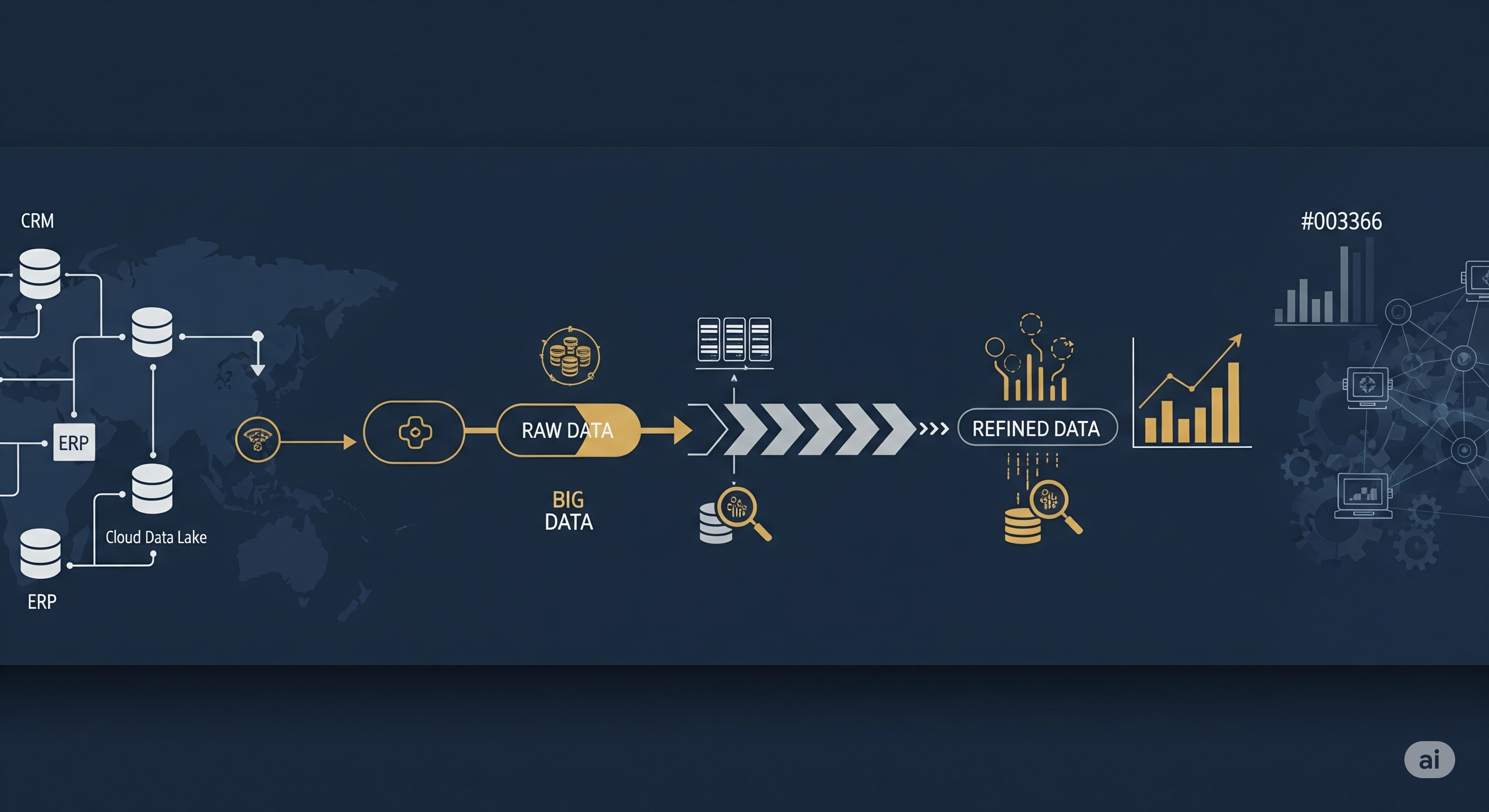
Unit 3: Data Pipeline
Key Concepts:
- Data ingestion, transformation, storage
- Monitoring, exploration, and quality control
- Pipeline scalability and cost efficiency
Reflections: This unit refined my understanding of data flow, and emphasised the role of pipelines in delivering high-quality, actionable insights, particularly concerning their support for Big Data and Master Data Management. I gained a better appreciation for the benefits, such as improved data quality and scalability, alongside the challenges in design and maintenance.
Related Work:
- 📄 Discussion Summary - Grade 65% (Merit)
Unit 4: Big Data Architecture
Key Concepts:
- Data Lakes vs Warehouses
- 4Vs: Volume, Variety, Velocity, Veracity
- Cloud integration and data mining
Reflections: Exploring big data architecture revealed the scalability and complexity of large-scale systems, and how data lakes and warehouses are designed to handle the 4Vs. The discussion around security concerns in cloud-based storage, such as data residency and access control for sensitive information, was particularly insightful, highlighting the need for robust governance in such environments and the critical importance of safeguards.
Unit 5: Analytics Tools
Key Concepts:
- Data analytics in enterprise strategy
- Tool selection and contextual use
- Relationship between analytics and EDA
Reflections: I explored tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Python-based analytics, building a clearer understanding of how analytical tools are used in different organisational scenarios. The link between analytics and enterprise architecture stood out, emphasising how crucial it is to choose the right tool for the right situation to impact decision-making across the business. The HBR article analysis offered practical insights into financial sector transformations.
Related Work:
Unit 6: Value of Data
Key Concepts:
- Data valuation models
- Direct vs indirect costs
- Enterprise data classification
Reflections: I learned to assess data’s financial value and propose strategies for extracting its business worth, distinguishing between direct and indirect costs of data and how they affect decision-making. The second assignment allowed me to apply EDA principles to real data by recommending an Enterprise Data Architecture for the Department of Traffic in London, highlighting the practical application of these concepts.
Related Work:
- 📄 Forum Post
- 📄 Evaluation Submission
- 📄 Assignment Report – London Traffic EDA - Grade 60% (Merit)
Unit 7: IP Strategy
Key Concepts:
- Data as Intellectual Property
- IP protection in digital ecosystems
- EDA as a strategic enabler
Reflections: I now appreciate how data assets can be protected and strategically managed to maintain competitive advantage, learning that data is a valuable asset within an Enterprise Data Architecture (EDA). This unit equipped me with an understanding of deploying EDA as a strategic tool for digital transformation, including safeguarding data assets and identifying complements that drive EDA.
Related Work:
Unit 8: Digital Transformation
Key Concepts:
- Drivers of digital convergence
- Transformation frameworks and models
- Required skills and capabilities
Reflections: Digital transformation is clearly more than a technology shift—it’s an organisational mandate, requiring a deep understanding of its foundations, requirements, models, and tools. This unit enhanced my strategic thinking on business change, especially concerning the essential skills needed to implement such transformations effectively.
Unit 9: Compliance & Ethics
Key Concepts:
- Regulatory and ethical frameworks
- Governance and compliance costs
- Risk mitigation and bottleneck management
Reflections: Understanding governance frameworks equips me to plan ethical, compliant data systems, particularly regarding the inherent challenges and substantial cost implications of implementing Governance and Compliance Frameworks. It also helped me appreciate the compliance officer’s critical role and develop strategies for mitigating implementation bottlenecks and making cost-effective decisions within an Enterprise Data Architecture (EDA) environment.
Unit 10: ITIL Framework
Key Concepts:
- ITIL lifecycle: Strategy → Design → Transition → Operation
- Relevance of ITIL to EDA
- IT service models and frameworks
Reflections: This unit introduced me to structured IT service management through the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL), encompassing its Services Strategy, Design, Transition, Operations, and Improvements. I now understand how ITIL integrates with enterprise data processes, recognising its pivotal role as a framework for organisational efficiency and critically evaluating the challenges associated with ITIL deployment.
Unit 11: Business Intelligence
Key Concepts:
- BI tools: data lakes, warehouses, analytics platforms
- Machine learning in BI
- Implementation bottlenecks
Reflections: This was a capstone unit linking earlier concepts, providing a focused examination of Business Intelligence (BI) tools and concepts. BI’s dependency on sound Enterprise Data Architecture (EDA) became especially clear during our third assignment, underscoring that a robust EDA serves as the foundational driver for effective BI and highlighting the critical challenges during implementation.
Related Work:
- 📄 Assignment – Enterprise Data Strategy - Grade 85% (Distinction)
Unit 12: ERP Systems
Key Concepts:
- ERP platforms: SAP, Oracle, Azure, InfoCloud
- ERP’s role in SCM and EDA
- Implementation costs and risks
Reflections: I explored how ERP systems act as operational backbones, powered by data architectures, examining various ERP tools and their functionalities. The ERP modelling exercise helped reinforce this relationship, and the unit also critically addressed the significant cost implications and inherent challenges associated with ERP implementation.
Related Work:
🏁 Summary of Achievements
- ✅ Completed 3 major assignments demonstrating applied EDA skills
- 💬 Contributed actively to student forums across 6+ units
- 🧠 Gained practical and theoretical understanding of BI, ERP, and data governance
- 🗂 Built and maintained a structured ePortfolio with critical reflections and artefacts